Focus on XWorm obfuscation 🪱
— pboXWorm is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) developed in .NET, the malware is mostly spread via phishing campaigns using homemade or opensource packing tools. Note, that some versions of the source code have leaked on Cybercrime forums and also on Telegram channels. This analysis focuses on the XWorm version 3.0.

TL;DR XWorm #
The malware has many functionalities: Virtual environment detection, command execution, file download/upload, persistent after reboot, keylogging, etc… An interesting feature of the RAT is the plugin configuration; attackers can configure plugins that are downloaded and executed by the RAT during the infection. The plugins are mainly DLL in .NET, the last section explains how to extract XWorm plugins from network capture.
The next sections detail how the RAT managed its configuration deobfuscation, then how the Command and Control (C2) communication works.
Links to download the sample used for this analysis:
- MalwareBaazar: SHA256-6f2e22d541680c151da164b02f916a3d72da0517b2f052f7356d05e8b374690b
- Tria.ge sandbox
The RAT have been spotted at the end of November 2022 distributed in malspam campaigns, as reported in this tweet:
Most people don't tag their precise location in Tweets, so we're removing this ability to simplify your Tweeting experience. You'll still be able to tag your precise location in Tweets through our updated camera. It's helpful when sharing on-the-ground moments.
— Twitter Support (@TwitterSupport) June 18, 2019
One reason of the rise of XWorm observed in the wild could be the leak of the source code:
- XSS forum:
xss.]is/threads/75837/; - Shinyenigma Github repository: Shinyenigma/XWorm-RAT.
XWorm data obfuscation #
The RAT configuration is stored in a class of the namespace Stub, where variables value are encoded in base64, in this version of the sample namespaces, classes
and variables names are randomized to slow down the analysis, however, the structure of the code remains the same as clear sample!
This naming randomization is becoming more and more popular amoung threat actors that have XWorm in their arsenal.
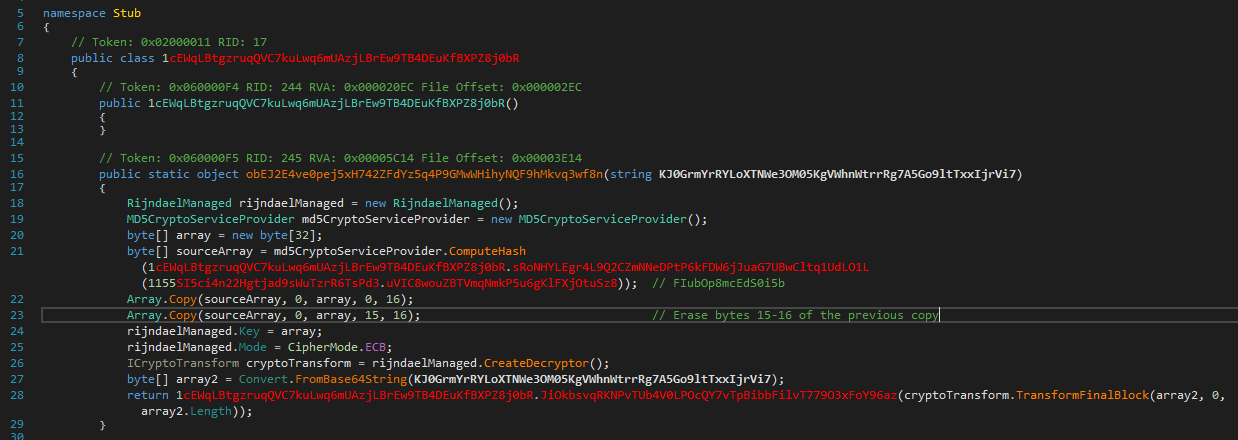
Figure 1: XWorm configuration decryption using AES (ECB No padding)
XWorm first deobufscates its configuration, it initiates a CryptServiceProvider,
then the RAT compute the MD5 hash of a variable (named Mutex) located in its configuration
class. Finally the hash is manipulated (oddly 🙃) to create the decryption key used to decrypt
the rest of configuration (host, port, etc.).
XWorm uses Rijndael The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard encryption in ECB (Electronic CodeBook) mode, no IV (Initial Vector) is required here. To create the key, the malware creates the MD5 hash of a variable copies the 8 first bytes to store them at the beginning of a new allocated array (of 16 bytes; the decryption key length), then re-copies these same 8 bytes to the key array but not after the 8 first bytes but from the 7^th byte to the 15 byte. The last byte (16^th) is zero (due to the array initialization). The figure below schematizes how the key is built.
+----------+ Base64 decode +--------+
| Variable +------------------>| Array |
+----------+ +-----+--+
|
+-MD5
|
+-----v--------------------------+
|dfe3ee833129588467dcf63d547b5806|
+--------------------------------+
0 8 16 (bytes)
+ -----+------- +
| Copy
+---------------+
| |
| v
| + --------------+
v |dfe3ee8331295884|
+--------------- +
|dfe3ee8331295884|
+--------------+-+---------------+--+
| |X| |00|
+--------------+-+---------------+--+
0 7 8 15 16 (bytes)
NB:
- the bytes 7 is overwritten
- the last byte of the key is fill with null byte
- the Rijndael key is 16 bytes long.
Code of the class in charge of the configuration ⤵️
|
|
In this version of the RAT variables name are obfuscated, the two highlighted variables are the communication key (first variable from the top)
and the second one is what was named Mutex. The mutex is the variable holding the base string
used to build the decryption key for the configuration. The variable holding the key used for communication encryption/decryption need
to be first decrypted by the same method used for the rest of the configuration decryption before behing used for the communication.
Once decrypted, the configuration of XWorm is:
| Purpose | Value obfuscated | Cleartext |
|---|---|---|
| C2 Host | VpmZ71vaW8IbCUUhXaZYmIZ+fg3gEPqzqfEpJeFIWv0= | names-again.at.playit.]gg |
| C2 Port | a6SLXA5CKiTAVsnJwB7XJw== | 59741 |
| AES key for communication | bvUFyfn2d6e7YEJt9/zw/A== | <123456789> |
| Message split pattern | suGMnRXFX/LRVfGLaUEsHA== | <Xwormmm> |
| Installation name | 5D+67sZ9S91x7RZPyaBWwBnRhFtzU62dUOgoP7j7MdQ= | Microsoft OneDrive.exe |
Here is the cyberchef recipe.
Command and Control Communication #
XWorm communications are encrypted with AES algorithm in ECB mode. The RAT uses raw TCP connection on a port defined by the attacker. Exchanged messages are not fully encrypted, in fact the first bytes contains the size of the message followed by a null bytes (used as a split pattern) in cleartext, see the figure below where the size of the message is in black, the split pattern in red and the encrypted message in blue.

Figure 2: XWorm raw TCP message in hexdump format
Once the mutex and the communication key are identified you can use this script to deobfuscate the RAT communication.
|
|
To dump the XWorm messages in cleartext from a PCAP, use the following command:
tshark -r /tmp/dump.pcapng -Y "tcp.port == 3395" -e tcp.payload -Tjson |
jq -r ".[]._source.layers[][]" |
python3 decrypt_xworm_com.py --mutex="FIubOp8mcEdS0i5b" --com="bvUFyfn2d6e7YEJt9/zw/A=="
This sample of XWorm communicates on port 3395.
b'INFO<Xwormmm>9623CE2085896DD4BD55<Xwormmm>Admin<Xwormmm> Windows 10 Pro 64bit<Xwormmm>XWorm V3.0<Xwormmm>23/02/2023<Xwormmm>False<Xwormmm>True<Xwormmm>False<Xwormmm>None'
b'PING!'
b'plugin<Xwormmm>179DCD0BAD17DB8E467A40D7B57437461CDC3263090966A687BDD40B279E4DF2<Xwormmm>0'
b'sendPlugin<Xwormmm>179DCD0BAD17DB8E467A40D7B57437461CDC3263090966A687BDD40B279E4DF2
...
XWorm plugins #
As introduced, XWorm has the capability to download and execute plugins. This mechanism is simple, here is its workflow:
- The C2 send available plugins:
plugin<Xwormmm>Id of the plugin<Xwormmm> - The RAT ask the C2 to send the plugin:
sendPlugin<Xwormmm>Id of the plugin - The C2 send the plugin:
savePlugin<Xwormmm>Id of the plugin<Xwormmm>\x00\xc2\x07\x00<DLL .NET >
Referred to Figure 2 where the last packet (in the figure) received by the infected host has a size of 420736 bytes,
in fact this is a plugin sent by the C2.
This sample of XWorm downloads a plugin name Recover.dll with the following SHA-256: 179dcd0bad17db8e467a40d7b57437461cdc3263090966a687bdd40b279e4df2,
the plugin attempts to loot passwords and other authentication items.
The script dumps messages whose size exceeds 1000 bytes into a file, which is useful to dump XWorm plugins downloaded from the C2.